Aufgabentypen anhand von Beispielen durchstöbern
Lösen eines 3x3-LGS (eindeutige Lsg.)
Beispiel:
Löse das folgende Lineare Gleichungssystem!
Lösung einblenden
langsame Rechnung einblenden·(I)
+ ·(II)
·(I)
·(III)
langsame Rechnung einblenden·(II)
·(III)
Zeile (III):
=
eingesetzt in Zeile (II):
| -
2
3
x2
=
-15
| : 3
x2
= -5
eingesetzt in Zeile (I):
4x1 -1(-5
) -4·(-2
) = 1
| -
13
4
x1
=
-12
| : 4
x1
= -3
L={(-3
|-5
|-2
)}
3x3-LGS (unendliche Lösungsmenge)
Beispiel:
Löse das folgende Lineare Gleichungssystem!
-3x1 +x2 +5x3 = 0 6x1 -3x2 +x3 = -3 -15x1 +7x2 +3x3 = 6
Lösung einblenden
-3x1 +x2 +5x3 = 0
6x1 -3x2 +x3 = -3
-15x1 +7x2 +3x3 = 6
langsame Rechnung einblenden2·(I)
+ 1·(II)
5·(I)
-1·(III)
-3x1 1x2 5x3 = 0
(
-6
+6
)x1 +(
2
-3
)x2 +(
10
+1
)x3 = (0
-3
)
(
-15
+15
)x1 +(
5
-7
)x2 +(
25
-3
)x3 = (0
-6
)
-3x1 +x2 +5x3 = 0
-1x2 +11x3 = -3
-2x2 +22x3 = -6
langsame Rechnung einblenden2·(II)
-1·(III)
-3x1 1x2 5x3 = 0
-1x2 11x3 = -3
+(
-2
+2
)x2 +(
22
-22
)x3 = (
-6
+6
)
-3x1 +x2 +5x3 = 0
-1x2 +11x3 = -3
0 = 0
Setze
x3
= t
eingesetzt in Zeile (II):
-1x2 +11·(0+t ) = -3
| -
0-
11
t
-1
x2
=
-3
-
11
t | :
(-1)
x2
= 3
+11
t
eingesetzt in Zeile (I):
-3x1 +(3
+11
t ) +5·(0+t ) = 0
| -
3
-
16
t
-3
x1
=
-3
-
16
t | :
(-3)
x1
= 1
+
16
3
t
L={(1
+
16
3
t|3
+11
t|0+t )}
Um die Zahlen noch etwas schöner zu machen ersetzen wir t durch t= 3s:
L={(1
+16
s|3
+33
s|0+3
s )}
3x3-LGS (mit Parameter rechts)
Beispiel:
Löse das folgende Lineare Gleichungssystem!
x1 -4x2 -1x3 = -23 -2x1 +5x2 +8x3 = 64 x1 -8x2 +19x3 = 60r +1
Lösung einblenden
x1 -4x2 -1x3 = -23
-2x1 +5x2 +8x3 = 64
x1 -8x2 +19x3 =
60r
+1
langsame Rechnung einblenden2·(I)
+ 1·(II)
1·(I)
-1·(III)
1x1 -4x2 -1x3 = -23
(
2
-2
)x1 +(
-8
+5
)x2 +(
-2
+8
)x3 = (
-46
+64
)
(
1
-1
)x1 +(
-4
+8
)x2 +(
-1
-19
)x3 = (
-23
+ (
-60r
-1
)
)
x1 -4x2 -1x3 = -23
-3x2 +6x3 = 18
+4x2 -20x3 =
-60r
-24
langsame Rechnung einblenden4·(II)
+ 3·(III)
1x1 -4x2 -1x3 = -23
-3x2 6x3 = 18
+(
-12
+12
)x2 +(
24
-60
)x3 = (
72
+ (
-180r
-72
)
)
x1 -4x2 -1x3 = -23
-3x2 +6x3 = 18
-36x3 = -180
r
Zeile (III):
-36x3 = -180
r
x3
= 5
r
eingesetzt in Zeile (II):
-3x2 +6·(5
r
) = 18
-3x2 +30
r
= 18
| +
-30
r
-3
x2
=
-30r
+18
| :
(-3)
x2
=
10r
-6
eingesetzt in Zeile (I):
x1 -4·(
10r
-6
) -1(5
r
) = -23
x1 + (
-40r
+24
) -5
r
= -23
| +
45r
-24
1
x1
=
45r
-47
| : 1
x1
=
45r
-47
L={(
45r
-47
|
10r
-6
|5
r
)}
 Klasse 5-6
Klasse 5-6
 Klasse 7-8
Klasse 7-8
 Klasse 9-10
Klasse 9-10
 Kursstufe
Kursstufe
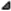 cosh
cosh
